Become a subscriber
Join our mailing list to discover new ways to optimize your health, feel incredible, and live longer
Picture this: you’re simply going about your day, maybe you just finished eating lunch or taking Fido for a walk. Suddenly, your arm starts to itch, and you see a red, bumpy rash that wasn’t there seconds ago. You’re trying to figure out what it is and what to do about it, and whether you need to go to an urgent care center, when it goes away as suddenly as it appeared.
What just happened? Chances are that it was urticaria.
Table of Contents
4. Potential Complications of Urticaria
6. What to Do if You’re Experiencing Urticaria
What Is Urticaria?
Urticaria is the clinical name for hives, which you may have heard of. It’s actually very common, affecting about 20% of people at some time in their lives. Urticaria is typically an allergic reaction.
Acute Urticaria vs. Chronic Urticaria
The vast majority of cases of hives are acute urticaria, like the situation we described above. Acute urticaria appears suddenly in response to a trigger, lasts for a short time (usually a matter of minutes or a few hours), and then disappears suddenly.
Less commonly, you could have chronic urticaria. In someone with chronic urticaria, hives appear and disappear daily or almost daily for six weeks or more. There usually isn’t an easily identifiable trigger, and your urticaria could recur for months or years. Chronic urticaria is fairly rare, though, affecting 0.5%-1% of the population.
Symptoms of Urticaria
How do you know if you’re experiencing urticaria? The symptoms are unique and identifiable. They include:
- Rash of itchy red bumps
- Rash that appears suddenly and lasts for a short time, usually minutes
- Rash that seems to appear frequently after you eat something specific or come into contact with a particular material
- Rash bumps that are red, but their centers turn white when you gently press them
A hives rash is somewhat distinctive, so once you have seen and experienced hives, you will typically recognize them if you have them again.
What Causes Urticaria?
Urticaria is generally an allergic reaction. It appears because of the chemicals your immune system releases when it fights off a perceived enemy. Those chemicals are called histamines, and they cause urticaria as well as other allergy symptoms like swelling, sneezing, and watery eyes.
Chronic urticaria, though, is unique. The rash usually can’t be tied to a specific allergen. It’s often associated with a hormonal condition like a thyroid imbalance or some other condition related to your immune system.
Common Triggers for Hives
Urticaria can be sparked by nearly any type of allergen, but there are some potential allergens that seem to trigger it more than others. Triggers for urticaria often include:
- Certain foods, especially foods that are common allergens like nuts, shellfish, or eggs
- Specific medications like aspirin, ibuprofen, or certain antibiotics
- Latex
- Pollen
- Pet dander
- Heat or cold
- Sun exposure
- Strenuous exercise
- Bacterial infections like strep throat or urinary tract infections
- Viral infections like the common cold, the flu, or COVID-19
- Certain plants
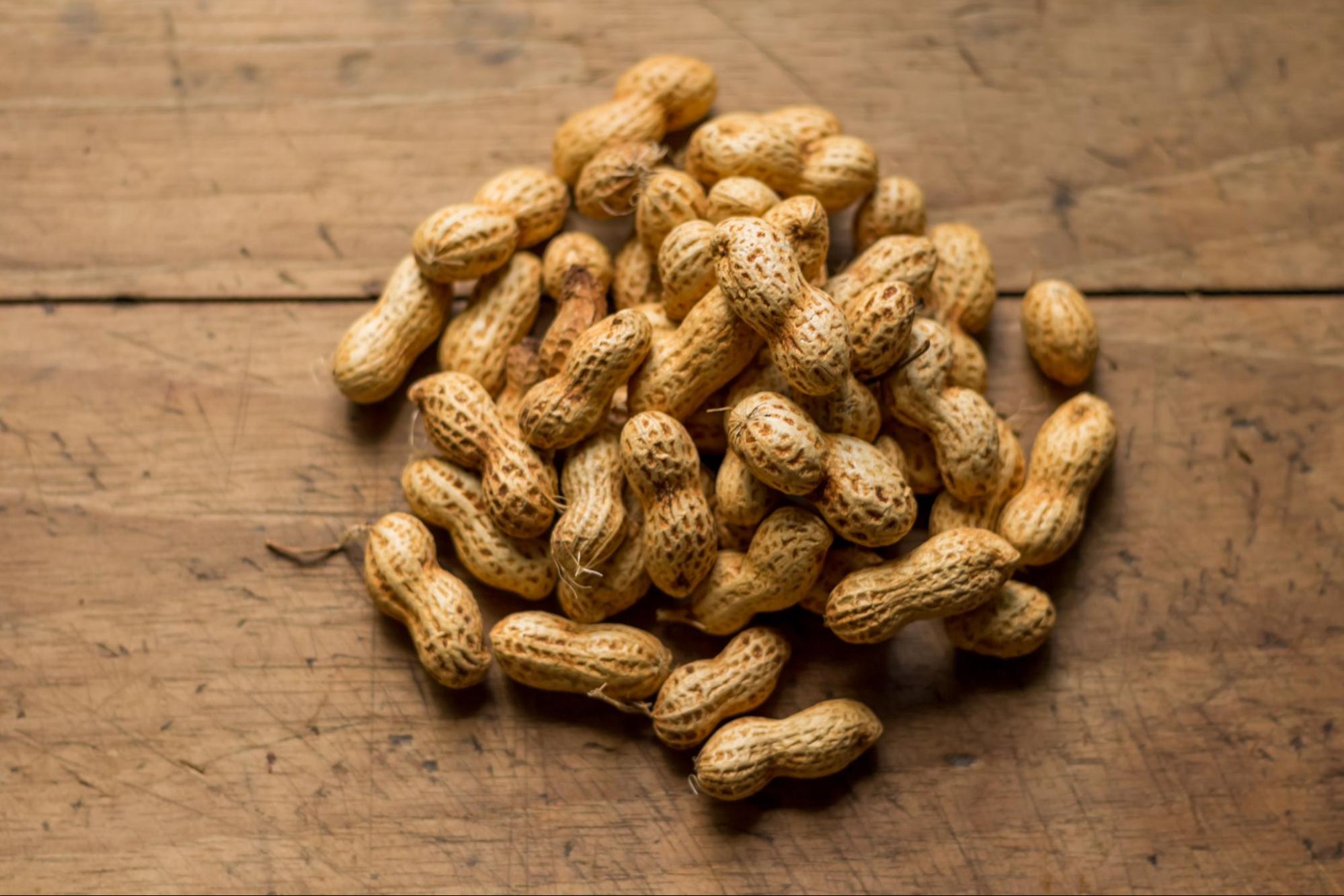


Clearly, this is a long list. It can be difficult to know what is triggering your urticaria, especially if the urticaria only appears once or twice and if you don’t have any known allergies.
Potential Complications of Urticaria
Urticaria is no picnic – it’s itchy and uncomfortable while your symptoms are present. Fortunately, it typically doesn’t lead to any serious threats to your health. Still, there are a few risks to keep in mind.
Throat Swelling
In rare cases, urticaria can appear in your throat, and it could swell in a way that narrows your airways, making it difficult to breathe. This is uncommon, but if it does happen, get emergency medical attention.
Infections
Urticaria is uncomfortably itchy, but it’s important to try not to scratch your rash. You could break the skin by scratching it, creating the opportunity for an infection of your skin. These infections can become serious, so be sure to get medical attention if you start to see signs of a skin infection.
Treatments for Urticaria
How can you treat or prevent urticaria? In many cases, an outbreak of hives is too short-lived for you to get medical treatment, but there are several ways to manage your symptoms at home and ways your doctor may treat your urticaria if it is a recurring problem.
Trigger Avoidance
It seems overly simple, but the best way to avoid the allergic reaction that triggers urticaria is to avoid the allergen. Of course, that requires finding out what your allergen is first. Your doctor may send you to an allergist for an allergy test.
In an allergy test, the allergist exposes your skin to a variety of potential allergens in controlled areas so they can observe how your skin reacts. Usually, this is done by simply scratching your skin with the allergen.
Allergy Treatment
Because urticaria is an allergic reaction, treatments to reduce your allergy symptoms can also reduce urticaria. If your allergen is something that isn’t truly avoidable, like sun exposure or pollen, your doctor may prescribe antihistamines that counteract the histamines your immune system releases.
For a more long-term solution, your allergist could perform immunotherapy. This is a lengthy process in which your allergist injects a small amount of your allergen on a regular basis. They increase the allergen little by little. Over time, this desensitizes your immune system to the allergen so your allergy symptoms (and your urticaria) are less significant.

Over-the-Counter Medications
When urticaria appears, you may be able to reduce your symptoms with over-the-counter medications like non-prescription antihistamines. Anti-itch creams can help as well. Be sure, though, that you ask a pharmacist or your doctor to make sure over-the-counter antihistamines won’t interact poorly with any prescriptions you’re already taking.
Corticosteroids
In severe episodes of urticaria, a doctor may use corticosteroids to quickly reduce the inflammation. This is rare, but it can be an option if, for example, your urticaria is narrowing your airway.
Cold Compresses
Whether or not you’re already taking prescription medications for your urticaria, a simple cold compress can help to soothe your symptoms at home. It can reduce the itching, inflammation, and discomfort during an urticaria outbreak. If your rash is widespread, a cool shower or bath can help too.
What to Do if You’re Experiencing Urticaria
If you’re struggling with urticaria, there is help available. At SRx, we take a holistic approach to your health, so your integrated care team can help you with long-term and short-term care for your urticaria. Schedule a virtual care appointment with our esteemed providers to get started.




